Published: 15 July 2025
Author: Jean Claude Munyakazi
Category: Network Management
Reading Time: 8 minutes
Last Updated: 31 August 2025
Network Management
A Practical Guide to Discovering, Maintaining, and Monitoring Your Network
Building Resilient and Secure Infrastructure
The Foundation of Modern Network Operations
Why Network Management Matters
Today’s networks support critical business operations, cloud services, IoT devices, and remote workforces. A single point of failure can cascade into significant downtime, security vulnerabilities, and financial losses. Effective network management provides:
- Proactive Issue Detection: Identify problems before they impact users
- Comprehensive Visibility: Understand your network topology and device relationships
- Operational Efficiency: Automate routine tasks and streamline troubleshooting
- Security Posture: Maintain configuration integrity and audit trails
- Business Continuity: Ensure rapid recovery from failures and disasters
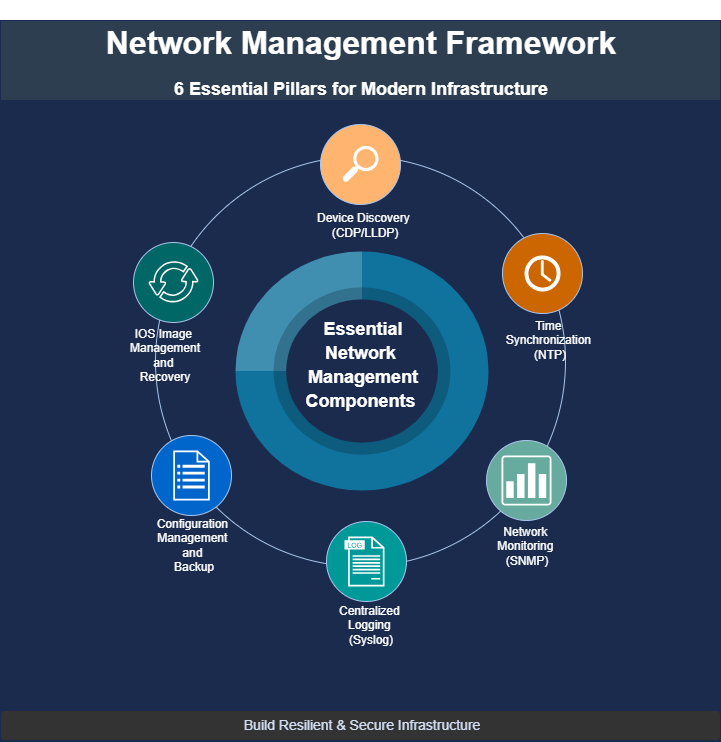
Essential Network Management Components
1. Discovering Devices with CDP and LLDP
Network discovery forms the foundation of topology mapping and relationship understanding. The Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) and Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) enable automatic neighbor discovery, providing administrators with real-time insights into device connectivity, capabilities, and network architecture.
2. Synchronizing Time with NTP
Accurate time synchronization is critical for log correlation, security protocols, and troubleshooting. Network Time Protocol (NTP) ensures all network devices maintain synchronized clocks, enabling precise event correlation and compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. Monitoring Devices with SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) serves as the universal language for network monitoring. By collecting performance metrics, status information, and alerts from network devices, SNMP enables proactive monitoring and automated response to network events.
4. Capturing Logs with Syslog
Centralized logging through Syslog provides comprehensive visibility into network events, security incidents, and operational activities. Effective log management enables rapid troubleshooting, security analysis, and compliance reporting.
5. Managing Configurations and Backups
Configuration management ensures network consistency, security, and recoverability. Automated backup systems, version control, and configuration compliance monitoring protect against human error and enable rapid disaster recovery.
6. IOS Image Management and Recovery
Software image management maintains network security and functionality through proper version control, testing procedures, and recovery mechanisms. This component ensures network devices run optimal software versions while providing fallback options during upgrades.
Multi-Vendor Network Reality
Modern enterprise networks rarely consist of equipment from a single vendor. Today’s infrastructure typically includes diverse technologies from Cisco, Juniper, HP/Aruba, Fortinet, Ubiquiti, MikroTik, and various virtual appliances. This multi-vendor reality requires administrators to master both proprietary tools and open standards.
The Power of Open Standards
While vendor-specific protocols like CDP offer enhanced functionality within homogeneous environments, open standards such as LLDP, NTP, SNMP, and Syslog provide universal compatibility across platforms. This standardization enables:
- Unified Management: Monitor and manage diverse equipment through common interfaces
- Vendor Independence: Avoid lock-in while maintaining operational flexibility
- Skill Transferability: Apply knowledge across different technology platforms
- Integration Capabilities: Connect disparate systems through common protocols
Building Your Network Management Strategy
Implementing effective network management requires a systematic approach that balances automation with human oversight. Success depends on understanding how these six components work together to create a cohesive management framework.
The journey toward network management excellence begins with mastering these fundamental building blocks. Each component contributes to overall network health, security, and performance, creating an infrastructure that can adapt to changing business requirements while maintaining operational stability.
Next Steps
Explore each of these critical network management areas in detail through my comprehensive guides. Whether you’re strengthening device discovery capabilities, implementing centralized monitoring, or developing robust backup strategies, these resources will help you build and maintain a world-class network infrastructure.
Ready to dive deeper? Click on any of the topics below to explore detailed implementation guides, best practices, and real-world examples that will elevate your network management capabilities.
1. Discovering Devices with CDP and LLDP
“Automate network topology mapping and device discovery using CDP and LLDP protocols for real-time insights”
2. Synchronizing Time with NTP
“Ensure precise time synchronization across network devices with NTP for accurate log correlation.”
3. Monitoring Devices with SNMP
“Monitor network performance and automate alerts using SNMP for proactive device management.”
4. Capturing Logs with Syslog
“Centralize network logging with Syslog for comprehensive visibility and rapid troubleshooting.”
5. Managing Configurations and Backups
“Automate network configuration backups and version control for consistency and disaster recovery.”
6. IOS Image Management and Recovery
“Manage network device software versions with proper testing and recovery mechanisms for upgrades.”
Network Management
Glossary of Core Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol) | A Cisco-proprietary Layer 2 protocol used to discover directly connected Cisco devices and gather basic information such as hostname and interface. |
| LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol) | A vendor-neutral Layer 2 discovery protocol used to identify neighboring devices in multi-vendor environments. |
| NTP (Network Time Protocol) | A protocol used to synchronize the clocks of devices across a network to a reference time source (e.g., GPS, atomic clock). |
| SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) | A protocol for monitoring and managing network devices, supporting actions like querying status (GET), setting configurations (SET), and receiving alerts (TRAP). |
| MIB (Management Information Base) | A structured database of network objects used by SNMP to represent device data in a hierarchical format via Object Identifiers (OIDs). |
| Syslog | A standardized logging protocol that enables network devices to send log messages to a centralized syslog server for monitoring and troubleshooting. |
| Severity Level (Syslog) | A numeric scale (0–7) assigned to syslog messages indicating the criticality of an event; 0 = Emergency, 7 = Debug. |
| Facility Code (Syslog) | An identifier that indicates the source subsystem of a syslog message (e.g., IP, OSPF, IF). |
| ROMMON (ROM Monitor) | A Cisco recovery mode used when the device cannot boot normally; commonly used for password recovery or system recovery. |
| TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) | A lightweight file transfer protocol used to backup or restore configurations and IOS images. |
| USB Flash (usbflash0:) | A file system reference for accessing USB storage on Cisco devices for transferring files and backups. |
| IOS (Internetwork Operating System) | The Cisco operating system used on routers and switches to manage networking functions. |
| boot system | A command used in Cisco IOS to set which image should be loaded during device startup. |
| confreg 0x2142 | A configuration register setting used in ROMMON to bypass loading the startup configuration file. |
| snmpget | A utility that retrieves SNMP object values from a device using OIDs. |
| OID (Object Identifier) | A unique identifier assigned to managed objects in a MIB hierarchy used in SNMP communication. |
