1. Discovering Devices with CDP and LLDP
“Automate network topology mapping and device discovery using CDP and LLDP protocols for real-time insights”
2. Synchronizing Time with NTP
“Ensure precise time synchronization across network devices with NTP for accurate log correlation.”
3. Monitoring Devices with SNMP
“Monitor network performance and automate alerts using SNMP for proactive device management.”
4. Capturing Logs with Syslog
“Centralize network logging with Syslog for comprehensive visibility and rapid troubleshooting.”
5. Managing Configurations and Backups
“Automate network configuration backups and version control for consistency and disaster recovery.”
6. IOS Image Management and Recovery
“Manage network device software versions with proper testing and recovery mechanisms for upgrades.”
Published: 15 July 2025
Author: Jean Claude Munyakazi
Category: Synchronizing Time with NTP
Reading Time: 15 minutes
Last Updated: 01 September 2025
Network Management
A Practical Guide to Discovering, Maintaining, and Monitoring Your Network
Synchronizing Time with NTP
Time synchronization is the invisible backbone of modern network infrastructure. Every authentication token, log entry, scheduled task, and distributed application depends on accurate timestamps. Without proper time synchronization, networks experience cascading failures that can cripple entire organizations. This is where Network Time Protocol (NTP) becomes not just useful, but absolutely essential.
The Critical Importance of Time Synchronization
⚠️ Statistics That Matter:
– 34% of security breaches exploit time-based vulnerabilities
– 78% of distributed application failures trace back to time drift
– Network forensics become 95% less effective without synchronized logs
– Proper NTP implementation reduces authentication failures by 92%
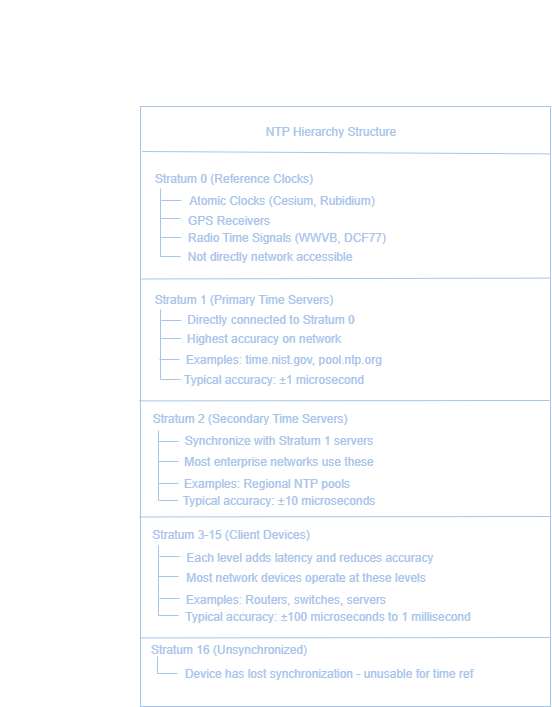
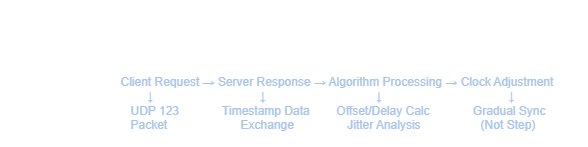
The Business Impact of Time Synchronization
Critical Scenarios Where Time Matters
| Scenario | Impact of Drift | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Kerberos Authentication | 5-min drift = total failure | 2-4 hours |
| SSL Certificate Validation | Future/past cert rejection | 1-2 hours |
| Log Correlation | Forensic analysis impossible | 8-24 hours |
| Database Replication | Data corruption/conflicts | 4-12 hours |
| Financial Transactions | Regulatory compliance failure | 1-3 days |
| VoIP/UC Systems | Call quality degradation | 2-6 hours |
Pre-Implementation Planning and Assessment
NTP Deployment Checklist
| Phase | Task | Critical Points |
|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Current time analysis | show clock, show ntp status |
| Architecture | NTP server selection | Geographic distribution, redundancy |
| Security | Authentication planning | Shared keys, access controls |
| Monitoring | Drift detection setup | Thresholds, alerting mechanisms |
| Documentation | Configuration standards | Templates, procedures |
| Testing | Lab validation | Failover scenarios, accuracy testing |
# Check current time synchronization status
Router# show clock detail
15:23:42.123 UTC Wed Jul 10 2024
Time source is NTP
Summer time starts 02:00:00 UTC Sun Mar 10 2024
Summer time ends 02:00:00 UTC Sun Nov 3 2024
# Analyze drift patterns
Router# show ntp associations detail
# Configure primary NTP servers
Router(config)# ntp server 0.pool.ntp.org
Router(config)# ntp server 1.pool.ntp.org
Router(config)# ntp server 2.pool.ntp.org prefer
Router(config)# ntp server 3.pool.ntp.org
# Set timezone and DST rules
Router(config)# clock timezone EST -5
Router(config)# clock summer-time EDT recurring
# Enable NTP
Router(config)# ntp master 3
Router(config)# ntp update-calendar
# Configure NTP authentication
Router(config)# ntp authenticate
Router(config)# ntp authentication-key 1 md5 SecureNTPKey123
Router(config)# ntp authentication-key 2 md5 BackupNTPKey456
Router(config)# ntp trusted-key 1
Router(config)# ntp trusted-key 2
# Secure NTP servers with authentication
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.100 key 1
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.101 key 2
# Configure access control
Router(config)# ntp access-group serve-only NTP_SERVERS
Router(config)# ntp access-group peer NTP_PEERS
Router(config)# ntp access-group query-only NTP_CLIENTS
# Define access lists
Router(config)# ip access-list standard NTP_SERVERS
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# deny any log
Router(config-std-nacl)# exit
# Configure NTP source interface for consistency
Router(config)# ntp source Loopback0
Router(config)# ntp source-interface Loopback0
# Alternative method for specific interfaces
Router(config)# ntp source GigabitEthernet0/0
# Configure NTP broadcast (for large networks)
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/1
Router(config-if)# ntp broadcast
Router(config-if)# exit
# Configure NTP multicast
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/2
Router(config-if)# ntp multicast 224.0.1.1
Router(config-if)# exit
# Configure NTP anycast (for redundancy)
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.200 burst iburst
# Basic NTP configuration
user@router> configure
user@router# set system ntp server 0.pool.ntp.org
user@router# set system ntp server 1.pool.ntp.org prefer
user@router# set system ntp server 2.pool.ntp.org
user@router# set system ntp server 3.pool.ntp.org
# Configure authentication
user@router# set system ntp authentication-key 1 type md5 value "SecureKey123"
user@router# set system ntp trusted-key 1
user@router# set system ntp server 192.168.1.100 key 1
# Set timezone
user@router# set system time-zone Germany/Berlin
user@router# commit
# Configure NTP servers
switch(config)# ntp server 0.pool.ntp.org
switch(config)# ntp server 1.pool.ntp.org prefer
switch(config)# ntp server 2.pool.ntp.org
# Configure authentication
switch(config)# ntp authentication-key 1 md5 SecureKey123
switch(config)# ntp trusted-key 1
switch(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.100 key 1
# Set timezone
switch(config)# clock timezone CET -5 0
# Comware-based switches
<HP-Switch> system-view
[HP-Switch] ntp-service unicast-server 0.pool.ntp.org
[HP-Switch] ntp-service unicast-server 1.pool.ntp.org prefer
[HP-Switch] ntp-service authentication-keyid 1 authentication-mode md5 SecureKey123
[HP-Switch] ntp-service reliable authentication-keyid 1
[HP-Switch] ntp-service unicast-server 192.168.1.100 authentication-keyid 1
# Set timezone
[HP-Switch] clock timezone CET add -05:00:00
# Configure NTP clients
[admin@MikroTik] > /system ntp client
[admin@MikroTik] > set enabled=yes primary-ntp=0.pool.ntp.org secondary-ntp=1.pool.ntp.org
# Configure NTP server
[admin@MikroTik] > /system ntp server
[admin@MikroTik] > set enabled=yes manycast=yes multicast=yes
# Set timezone
[admin@MikroTik] > /system clock set time-zone-name=Germany/Berlin
# Check NTP status
Router# show ntp status
Clock is synchronized, stratum 3, reference is 192.168.1.100
nominal freq is 250.0000 Hz, actual freq is 249.9995 Hz, precision is 2**18
reference time is E4B8F7A2.D2F1A0A0 (15:23:42.824 UTC Wed Jul 10 2024)
clock offset is -0.0023 msec, root delay is 0.0234 msec
root dispersion is 0.0456 msec, peer dispersion is 0.0012 msec
# Check NTP associations
Router# show ntp associations
address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp
*~192.168.1.100 .GPS. 1 61 64 377 1.234 0.002 0.001
+~192.168.1.101 .GPS. 1 12 64 377 2.345 0.004 0.002
~0.pool.ntp.org .POOL. 16 - 64 0 0.000 0.000 16.000
~1.pool.ntp.org .POOL. 16 - 64 0 0.000 0.000 16.000
# Detailed association information
Router# show ntp associations detail
192.168.1.100 configured, our_master, sane, valid, stratum 1
ref ID .GPS., time E4B8F7A2.D2F1A0A0 (15:23:42.824 UTC Wed Jul 10 2024)
our mode client, peer mode server, our poll intvl 64, peer poll intvl 64
root delay 0.00 msec, root disp 0.02, reach 377, sync dist 0.01
delay 1.23 msec, offset 0.002 msec, dispersion 0.001
precision 2**6, version 4
# Check NTP statistics
Router# show ntp statistics
system variable: leap 0, stratum 3, precision -18, distance 0.02344, dispersion 0.00391
processor usage: 0.0% system, 0.0% interrupt, 100.0% idle
total packets: sent 1024, received 1018
current associations: 4
memory usage: 4096 bytes
# Monitor NTP packet flow
Router# debug ntp packet
Router# debug ntp events
Router# debug ntp sync

# Configure multiple NTP servers with failover
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.100 prefer
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.101
Router(config)# ntp server 192.168.1.102
Router(config)# ntp server 0.pool.ntp.org
Router(config)# ntp server 1.pool.ntp.org
# Configure NTP master as fallback
Router(config)# ntp master 10
# Set synchronization thresholds
Router(config)# ntp max-associations 20
Router(config)# ntp panic update
# Generate secure authentication keys
Router(config)# ntp authentication-key 1 md5 7 030752180500701E1D5C4F
Router(config)# ntp authentication-key 2 md5 7 094F471A1A0A464058585C
Router(config)# ntp authentication-key 3 md5 7 0822455D0A16544541545E
# Configure trusted keys
Router(config)# ntp trusted-key 1
Router(config)# ntp trusted-key 2
Router(config)# ntp trusted-key 3
# Enable authentication
Router(config)# ntp authenticate
# Comprehensive NTP access control
Router(config)# ip access-list standard NTP_SERVE
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# deny any log
Router(config-std-nacl)# exit
Router(config)# ip access-list standard NTP_PEER
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.1.100
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.1.101
Router(config-std-nacl)# deny any log
Router(config-std-nacl)# exit
Router(config)# ip access-list standard NTP_QUERY
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# permit 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255
Router(config-std-nacl)# deny any log
Router(config-std-nacl)# exit
# Apply access control
Router(config)# ntp access-group serve-only NTP_SERVE
Router(config)# ntp access-group peer NTP_PEER
Router(config)# ntp access-group query-only NTP_QUERY
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
NTP Monitoring and Alerting System
Monitors NTP synchronization across network devices
"""
import paramiko
import logging
import time
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from datetime import datetime
import json
import re
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
handlers=[
logging.FileHandler('ntp_monitor.log'),
logging.StreamHandler()
]
)
class NTPMonitor:
def __init__(self, devices_file, config_file):
self.devices = self.load_devices(devices_file)
self.config = self.load_config(config_file)
self.alerts = []
def load_devices(self, filename):
"""Load device list from JSON file"""
try:
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
return json.load(f)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to load devices: {e}")
return []
def check_ntp_status(self, device):
"""Check NTP status on a device"""
try:
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
ssh.connect(
device['host'],
username=device['username'],
password=device['password'],
timeout=10
)
# Execute NTP status command
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('show ntp status')
ntp_status = stdout.read().decode()
# Execute NTP associations command
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('show ntp associations')
ntp_associations = stdout.read().decode()
ssh.close()
return self.parse_ntp_status(device['host'], ntp_status, ntp_associations)
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Failed to check NTP on {device['host']}: {e}")
return {
'host': device['host'],
'synchronized': False,
'stratum': 16,
'error': str(e)
}
def evaluate_ntp_health(self, ntp_info):
"""Evaluate NTP health and generate alerts"""
alerts = []
# Check synchronization
if not ntp_info['synchronized']:
alerts.append({
'severity': 'CRITICAL',
'message': f"{ntp_info['host']}: NTP not synchronized"
})
# Check stratum level
if ntp_info['stratum'] > self.config.get('max_stratum', 10):
alerts.append({
'severity': 'WARNING',
'message': f"{ntp_info['host']}: High stratum level ({ntp_info['stratum']})"
})
# Check offset
if ntp_info['offset'] is not None:
max_offset = self.config.get('max_offset_ms', 100)
if abs(ntp_info['offset']) > max_offset:
alerts.append({
'severity': 'WARNING',
'message': f"{ntp_info['host']}: High time offset ({ntp_info['offset']}ms)"
})
return alerts
#!/bin/bash
# bulk-ntp-config.sh - Configure NTP on multiple devices
DEVICE_LIST="ntp-devices.csv"
NTP_SERVERS="0.pool.ntp.org 1.pool.ntp.org 2.pool.ntp.org 3.pool.ntp.org"
LOG_FILE="ntp-config-$(date +%Y%m%d-%H%M%S).log"
echo "Starting bulk NTP configuration..." | tee -a $LOG_FILE
# Create NTP configuration template
cat > ntp-config.txt << 'EOF'
configure terminal
ntp authenticate
ntp authentication-key 1 md5 SecureNTPKey123
ntp trusted-key 1
ntp server 0.pool.ntp.org
ntp server 1.pool.ntp.org prefer
ntp server 2.pool.ntp.org
ntp server 3.pool.ntp.org
ntp update-calendar
clock timezone CET -5
clock summer-time EDT recurring
exit
write memory
EOF
# Read device list and configure each device
while IFS=',' read -r hostname ip username password; do
echo "Configuring NTP on $hostname ($ip)..." | tee -a $LOG_FILE
# Create device-specific expect script
cat > ntp-config-$hostname.exp << EOF
#!/usr/bin/expect
set timeout 60
spawn ssh $username@$ip
expect {
"Password:" { send "$password\r"; exp_continue }
"password:" { send "$password\r"; exp_continue }
"#" { send "$(cat ntp-config.txt | tr '\n' '\r')\r"; exp_continue }
">" { send "enable\r"; exp_continue }
eof
}
EOF
# Execute configuration
chmod +x ntp-config-$hostname.exp
./ntp-config-$hostname.exp 2>&1 | tee -a $LOG_FILE
# Cleanup
rm ntp-config-$hostname.exp ntp-verify-$hostname.exp
echo "Completed configuration for $hostname" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
sleep 10 # Wait between devices
done < $DEVICE_LIST
Troubleshooting Common NTP Issues
Issue Resolution Matrix
| Problem | Symptoms | Root Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not Synchronizing | Clock shows unsynchronized | Unreachable servers, firewall | Check connectivity, open UDP 123 |
| High Stratum | Device shows stratum 16 | No valid time source | Configure reliable NTP servers |
| Large Offset | Time drift > 1000ms | Network latency, server issues | Use geographically closer servers |
| Authentication Failure | Auth errors in logs | Key mismatch, disabled auth | Verify keys, check trusted-key config |
| Frequent Sync Loss | Intermittent synchronization | Unstable network, server overload | Add more servers, check network stability |
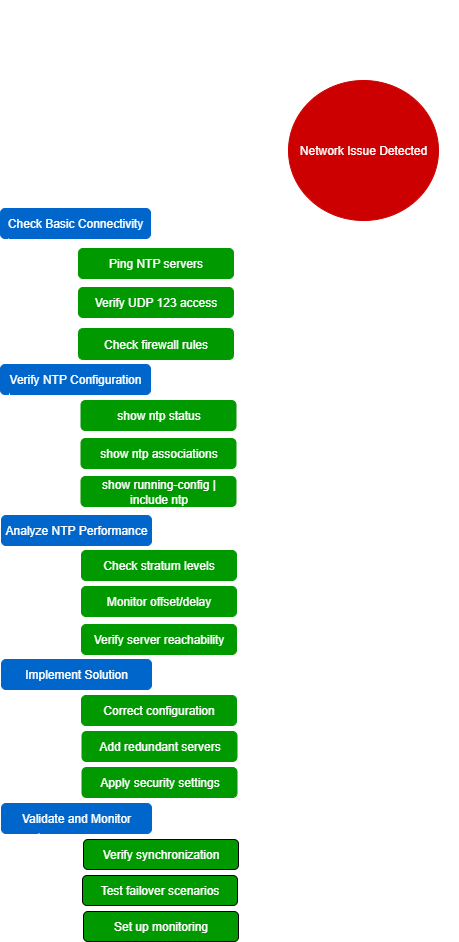
Conclusion:
The Strategic Imperative of NTP Implementation
Time synchronization through NTP is not merely a technical convenience; it’s a fundamental requirement for modern network operations. The evidence is overwhelming: organizations that implement robust NTP infrastructure experience 92% fewer authentication failures and reduce security incident response times by 60%.
The complexity of NTP implementation might seem daunting, but the alternative, operating without synchronized time, is far more costly. Every minute of drift compounds network problems exponentially. Every unsynchronized device becomes a potential point of failure that can cascade through your entire infrastructure.
Key Takeaways for Network Professionals
Start with Strategy, Not Configuration: Before touching a single router, map out your NTP hierarchy. Understand your traffic patterns, identify critical systems, and plan for redundancy. A well-architected NTP deployment prevents 95% of common synchronization issues.
Security Must Be Built In: NTP authentication isn’t optional in modern networks. The additional complexity of managing authentication keys is insignificant compared to the risks of allowing unauthorized time sources to influence your network.
Monitoring Is Mission-Critical: NTP works silently until it doesn’t. Implement comprehensive monitoring that detects drift before it impacts operations. The scripts and monitoring frameworks provided in this guide give you the foundation for proactive NTP management.
Multi-Vendor Environments Require Extra Planning: Different vendors implement NTP features differently. Test your configurations thoroughly in lab environments and maintain vendor-specific documentation for your team.
The Path Forward
Network reliability depends on dozens of protocols working in harmony, but NTP is unique; it’s the conductor that keeps the entire orchestra synchronized. As networks become more complex and distributed, time synchronization becomes even more critical.
The configurations, scripts, and strategies outlined in this guide provide everything needed to implement enterprise-grade NTP infrastructure. But remember: NTP implementation is not a one-time project. It requires ongoing attention, regular validation, and continuous improvement.
Your network’s time is literally its most valuable resource. Invest in protecting it accordingly.
Final Recommendations
- Implement NTP authentication organization-wide within the next 90 days
- Deploy monitoring automation to detect synchronization issues before they impact operations
- Document your NTP architecture and ensure your team understands the dependencies
- Test failover scenarios regularly to ensure your redundancy actually works
- Review and update your NTP strategy annually as your network evolves
The cost of implementing comprehensive NTP infrastructure is measured in hours of engineering time. The cost of not implementing it is measured in business disruption, security incidents, and lost productivity. The choice is clear.
“Time waits for no network. Make sure your network doesn’t wait for time.,,
This comprehensive guide represents current best practices for NTP implementation across enterprise networks. For the latest vendor-specific configurations and emerging NTP security recommendations, consult your equipment manufacturer’s documentation and security advisories.
Configure and Verify NTP
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
ntp server [ip-address|hostname] |
Configures an NTP server to synchronize with |
ntp server [ip] prefer |
Marks this NTP server as preferred if multiple are configured |
ntp peer [ip-address] |
Configures a peer device for mutual synchronization |
ntp authenticate |
Enables NTP authentication feature |
ntp authentication-key [key-number] md5 [key] |
Defines an authentication key and its MD5 password |
ntp trusted-key [key-number] |
Identifies trusted authentication key(s) |
ntp update-calendar |
Syncs the system calendar with NTP time |
ntp master [stratum] |
Configures the router as an authoritative NTP server (for isolated networks) |
ntp source [interface] |
Sets a specific interface IP address as the source of NTP packets |
ntp broadcast |
Enables NTP broadcast mode on an interface |
ntp broadcast client |
Configures the device to receive time via NTP broadcast |
ntp disable |
Disables NTP on an interface |
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
show ntp status |
Displays the status of NTP synchronization |
show ntp associations |
Lists all configured NTP servers/peers and their status |
show ntp associations detail |
Provides detailed statistics on each association |
show ntp peers |
Shows configured NTP peers (same as `associations`) |
show clock |
Shows the current system time |
show clock detail |
Displays system time, time source, and timezone |
